| Source | Peters, Christoph, and Jan Marco Leimeister. “TM3-A Modularization Method for Telemedical Services: Design and Evaluation.” Proceedings of 21st European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS). 2013. |
|---|---|
| Use | The method was specifically designed for the service domain (telemedical services). Therefore, it already incorporates important aspects of services e.g. process orientation, intangibility and interactions with the customer. |
| Idea | The method is offering a stepwise support for the whole modularization process, from the information capturing, over the decomposition of services up to the actual module creation with the subsequent testing phase. An important advantage of this method is the provided information about which inputs and outputs are created at each of the five phases. However, the TM3 method is more an advice on what steps to undertake rather than on how to execute those steps. |
| Phases in the modularization process | Information capturing (partly) → Decomposition → Structuring→ Module Creation→ Testing (partly) |
| Structure of the modules | Temporal structure (Process) |
| Input | Data from quantitative Datasets (Interviews, surveys, etc.) |
| Output | Modularized service with interface specifications for each module |
| Application
requirement |
In the first phase, it is important to define who shall be surveyed and what questions are to be used, in order to get the necessary information. For the modelling of the second phase BTPM-knowledge (or any alternatives) is required. The testing phase was discussed only briefly in the paper, without clarifying how the quality of the resulting modular service is to be measured. |
| Algorithm | 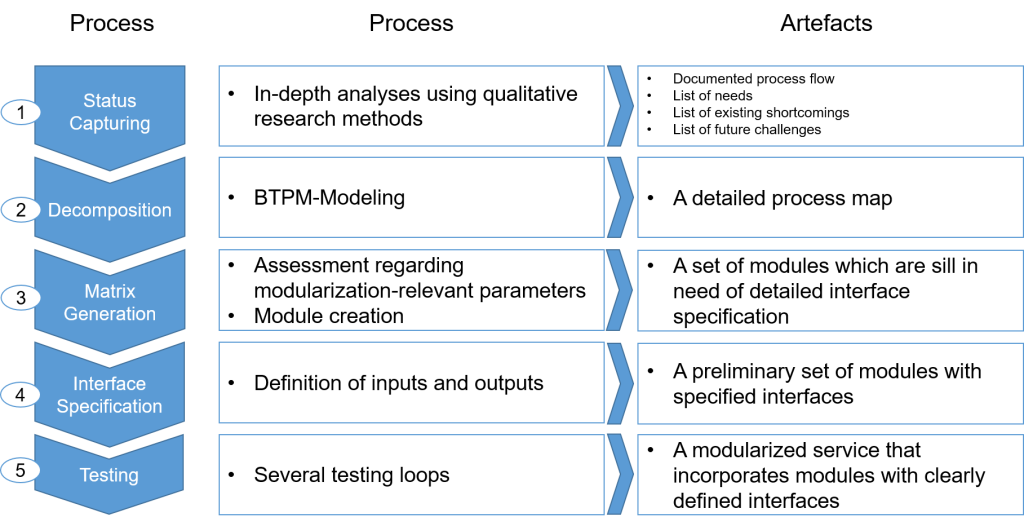 |
| Conclusion | Advantages: This method was originally developed for the service domain and contains almost every logical step of the modularization process. Moreover, TM3 provides additional information about how the single phases are interconnected (e.g. which artifacts are created and where are they to be used later) as well as which activities are going to be performed.
Disadvantages: Although the method presents the single steps of the modularization process, the implementation is not discussed. The matrix creation step presented in the paper is based on addition of values of different dimensions (e.g. “geographical differences” + “know-how level”), which should be scrutinized carefully. |