| Source | Steward, Donald V. “The design structure system: a method for managing the design of complex systems.” Engineering Management, IEEE Transactions on 3 (1981): 71-74. |
|---|---|
| Use | DSM is applied in the product development to identify potential for development. It aims knowledge storing, increasing product understanding and improving product development. |
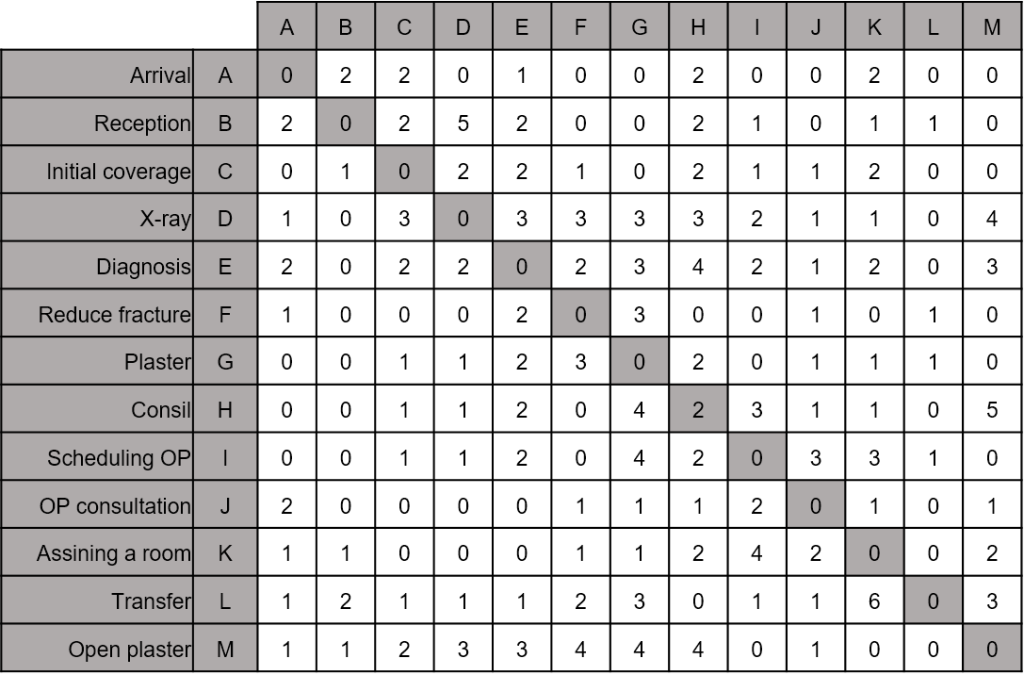
| Idea | DSM captures the dependences between singular standardizable performance components. Those components form the service. They are placed in the lines and the columns to generate an array.
In this array, possible dependences can be rated, e.g. quantitative -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 (dependent on the strength of those relations or showing if those relations are useful or undesirable). |
| Phases of modularization | Structuring |
| Input | Services which are already disassembled in individual components |
| Output | Array of dependences, which contains the interdependencies and their strengthens |
| Condition for the application | The DSM method requires a list of clear defined components, which are also separated from each other. It does not consider the way of decomposition for the single elements, components or functions. Their existing mutual dependences or interactions have to be rated with the help from experts using expert talks for example. |
| Approach | 0. Decomposition of the service in single performance components 1. Deduction of a relationship array from the first DSM with information about:
2. Those results generate the input for additional algorithms and construction rules, which enable the module generation. For example combination rules for components for module generation. A mathematic approach is shown by Carsten and Salewski (2013). They see the problem as an assignment- or an current problem. |
| Conclusion | Disadvantages: The DSM method gives no information about the essential decomposition of the service. It does not deliver singular modules. Because of that, the method can only be used as an interim stage or as an input for following (mathematical) procedures. Advantages: DSM generates a simple overview about the relations between the performance elements or components. Additionally DSM could prevent quantitative information if it is required. |