| Source | Stone, Robert B., Kristin L. Wood, and Richard H. Crawford. “A heuristic method for identifying modules for product architectures.” Design studies 21.1 (2000): 5-31. |
|---|---|
| Use | Developed originally for the context of tangible goods (e.g. drilling machine), but can be also applied for the service section, if appropriate “flows” are identified, e.g. flow of information or flow of resources. |
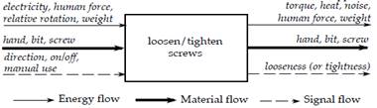
| Idea | Using Functional Decomposition the overall functionality is divided into smaller easier to solve sub-functions, which can be represented in the form of a Black Box. The relevant flows can be further differentiated in e.g. energy flow, material flow or signal flow.
There are three variants of how modules can be identified: Dominant Flow, Branching Flow and Conversion Transmission. It is recommended to simulate all the variants to identify all the possible module combinations. |
| Phases in the modularization process | Decomposition → Structuring → Module Creation |
| Module structure | Temporal structure (process) |
| Input | Flow chart of a functional decomposed service |
| Output | Modules (consisting of different functions) |
| Application requirement | A complete, functional model is required, which decomposes the overall functionality on a very detailed level, which requires a high level of expertise. |
| Algorithm |
|
| Conclusion | Advantages: This method can be used to identify new modules and product innovation in general. However, this is possible only in the case, if the appropriate flows are defined specifically for services.
Disadvantages: In order to represent the connections and interdependencies of the product, the flow diagram has to be created on a very detailed level with the help of domain experts. Furthermore, it remains unclear what granularity level of the diagram is desired. This method can be simply applied for tangible goods, because technical aspects are clearly connected to each other. In services, however, complications may arise, due to the fact that processes cannot be separated that easily. |